Recently, we worked on a requirement that required us to deal with temporary data storage. This is when we started inserting data into our temp table. During this journey, we identified a few simple and easy-to-use approaches. In this article, we will discuss all those approaches to inserting data into the temp table in the SQL server.
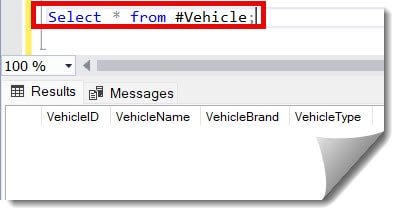
Let us consider an example to illustrate this scenario. I have an existing table named #Vehicle. It is empty, as shown in the screenshot below.
Approach-1: Using the INSERT INTO statement
We can execute the below SQL query to insert the value.
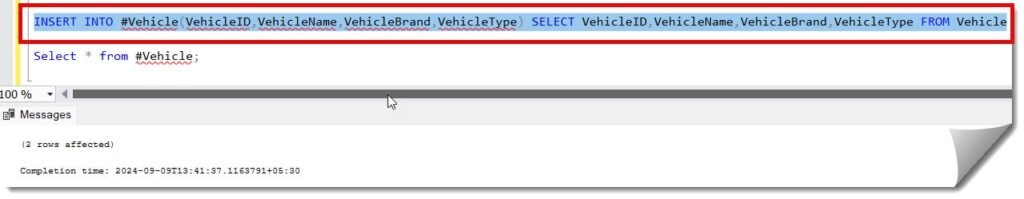
INSERT INTO #Vehicle(VehicleID,VehicleName,VehicleBrand,VehicleType) SELECT VehicleID,VehicleName,VehicleBrand,VehicleType FROM VehicleAfter executing the above query, the query was executed successfully, as shown in the screenshot below.
Check out How to create a temp table in SQL Server
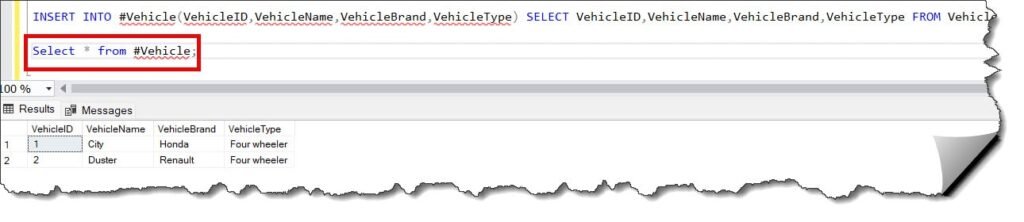
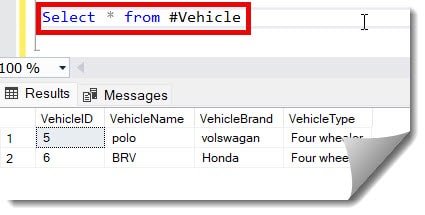
Now, let us verify with the select statement if the values exist. The values are shown in the screenshot below.
You can also use the below query to insert values explicitly and not from the source table.
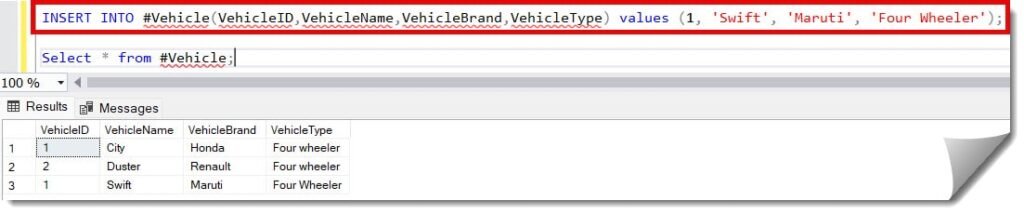
INSERT INTO #Vehicle(VehicleID,VehicleName,VehicleBrand,VehicleType) values (1, 'Swift', 'Maruti', 'Four Wheeler');After executing the above query, the explicit value is successfully inserted into the table, as shown in the screenshot below.
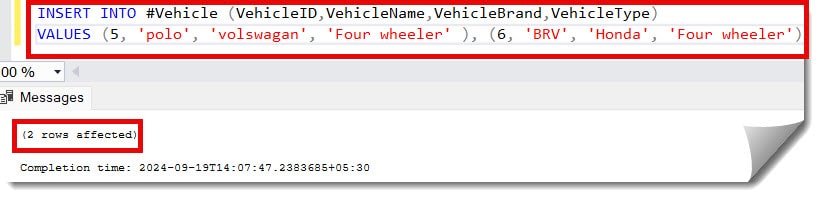
You can execute the below query to insert multiple records at once.
INSERT INTO #Vehicle (VehicleID,VehicleName,VehicleBrand,VehicleType)
VALUES (5, 'polo', 'volswagan', 'Four wheeler' ), (6, 'BRV', 'Honda', 'Four wheeler')After executing the above query, I got the expected output, as shown below.
Check out How to drop temp table if exists in SQL Server
Approach-2: Using the SELECT INTO statement
You can use the Select into statement to create a brand new temp table with the existing data and structure from the Parent table.
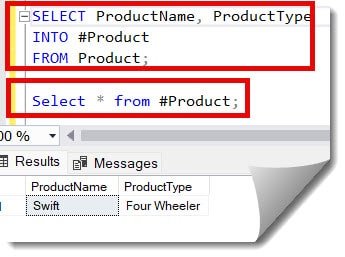
SELECT ProductName, ProductType
INTO #Product
FROM Product;After executing the above query, I got the expected output, as shown in the screenshot below.
Check out How To Check SQL Server Version
Approach-3: Using the CREATE TABLE statement
You can also use the Create Table statement followed by the Insert into statement.
Syntax
CREATE TABLE #TempTable (Firstcolumn datatype, secondcolumn datatype)
INSERT INTO #VehicleNew (Firstcolumn, secondcolumn)
SELECT Firstcolumn, secondcolumn FROM YourOriginalTableNameExample
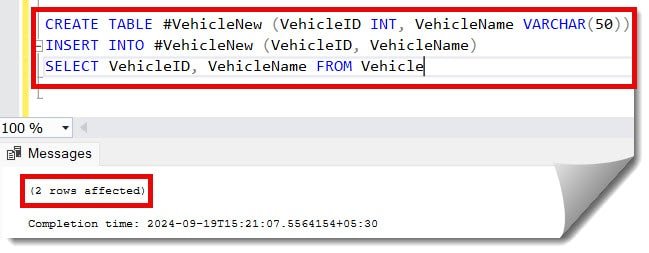
Let us execute the below query to create a table #VehicleNew and insert the data from the Vehicle table.
CREATE TABLE #VehicleNew (VehicleID INT, VehicleName VARCHAR(50))
INSERT INTO #VehicleNew (VehicleID, VehicleName)
SELECT VehicleID, VehicleName FROM VehicleAfter executing the above query, I got the expected output below.
Conclusion
Inserting data into our temporary tables in SQL Server is a potent technique that offers numerous benefits regarding data manipulation and query optimization. As discussed in this article, we can easily insert data to our temp table using the Insert into and Select into statements!
You can also follow the articles below.
- How to create index on temp table in SQL Server
- How to find column name in table SQL Server
- How to check if column exists in SQL Server database
- How to change column name in SQL Server

Grey is a highly experienced and certified database expert with over 15 years of hands-on experience in designing, implementing, and managing complex database systems. Currently employed at WEX, USA, Grey has established a reputation as a go-to resource for all things related to database management, particularly in Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle environments. He is a Certified Microsoft SQL Server Professional (MCSE: Data Management and Analytics) and Oracle Certified Professional (OCP), with Extensive database performance tuning and optimization knowledge and a proven track record in designing and implementing high-availability database solutions.